BREAST LIFT (MASTOPEXY)
Dr Chia Hui Ling
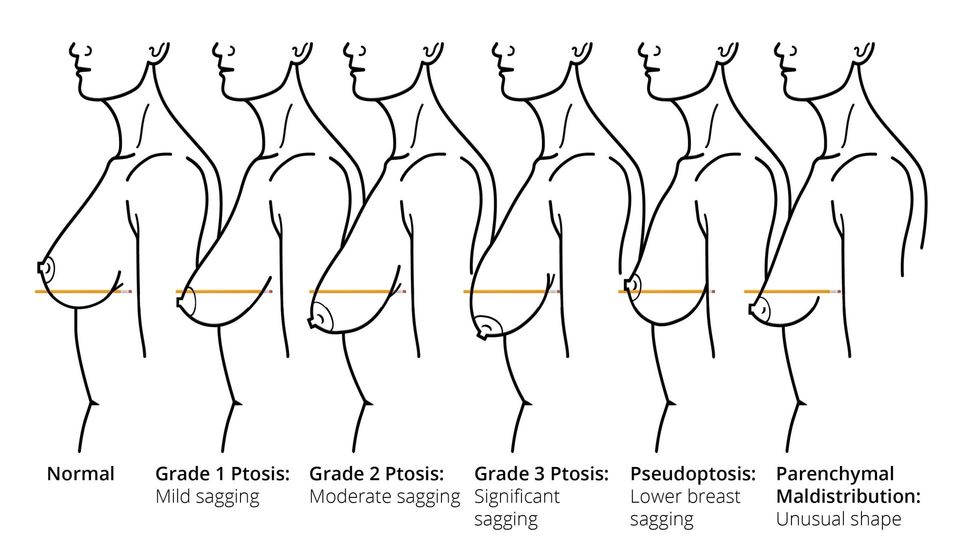
Breast lift, or mastopexy, is a surgical procedure to correct breast ptosis, or sagging breasts. Although tissue descent is a natural consequence of aging, development of breast ptosis is accelerated or exacerbated by factors such as larger breasts, breastfeeding, thin skin/weak tissues and weight fluctuations. The severity of ptosis is classified according to the level of nipple, relative to the inframammary fold (lower breast crease).
Grades of Breast Ptosis
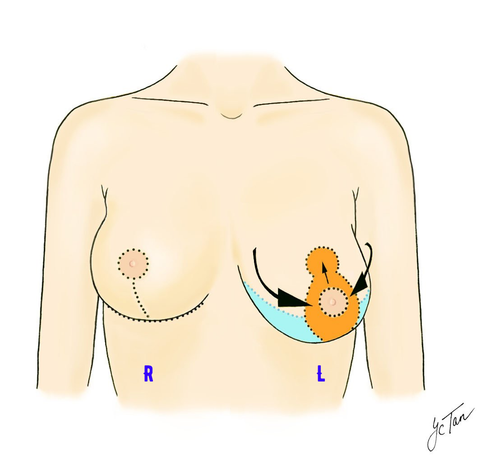
In this diagram, the possible scar positions are shown on the right breast (R). In general, more / longer scars are expected if there is more severe ptosis present.
On the left breast (L), the coloured areas represent the skin that may be removed during a mastopexy to lift the breast.
Augmentation Mastopexy
In mild cases of breast ptosis, breast augmentation
with implants alone
can offer a modest breast lift without the need for a mastopexy.
Breast deflation often accompanies breast ptosis and an augmentation mastopexy is suitable for those looking for both a breast lift and an increase in breast volume. Breast augmentation
and mastopexy are often carried out together in the same setting, but some plastic surgeons may elect to stage the augmentation mastopexy and do them on separate occasions. Fat grafting
is another option to augment the breast in a mastopexy.
TREATMENT
Have a thorough discussion with your plastic surgeon, including your surgical goals, medical conditions, drug allergies, medications and previous surgeries. Expected outcomes, such as breast size and scar placement, risks and other treatment options (like breast augmentation
and fat grafting) should be explained to you.
COMPLICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT
Risks of Mastopexy include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Poor wound healing
- Nipple numbness
- Nipple necrosis
- Breast lumpiness
- Unsatisfactory results, such as asymmetry or poor shape
- Unfavorable scarring
- Need for revision surgery